The housing affordability crisis in America is a growing concern that reflects broader economic challenges, including the impact of NIMBY policies and stringent land-use regulations. As many individuals are increasingly priced out of the housing market, ownership becomes a distant dream for a significant portion of the population. This alarming trend has been further exacerbated by a decline in construction productivity, which has stagnated since the 1970s. Factors such as rising labor and material costs, compounded by housing crisis impacts, complicate efforts to find workable solutions. As communities grapple with escalating housing prices, addressing these pressing housing market challenges is imperative for sustaining economic stability and fostering social equity.
The current situation regarding affordable housing presents a formidable dilemma in the United States, where many find themselves unable to secure reasonable accommodations. The phenomenon of rising property costs, often linked to local opposition to new developments and restrictive zoning laws, has resulted in significant barriers to homeownership. Furthermore, diminished productivity within the construction sector adds another layer of complexity to the issue. These intertwined factors illustrate a critical need for innovative approaches to reinvigorate housing supply amid ongoing residential market pressures. Understanding the nuances of this crisis is essential for developing effective policies that foster inclusive community growth.
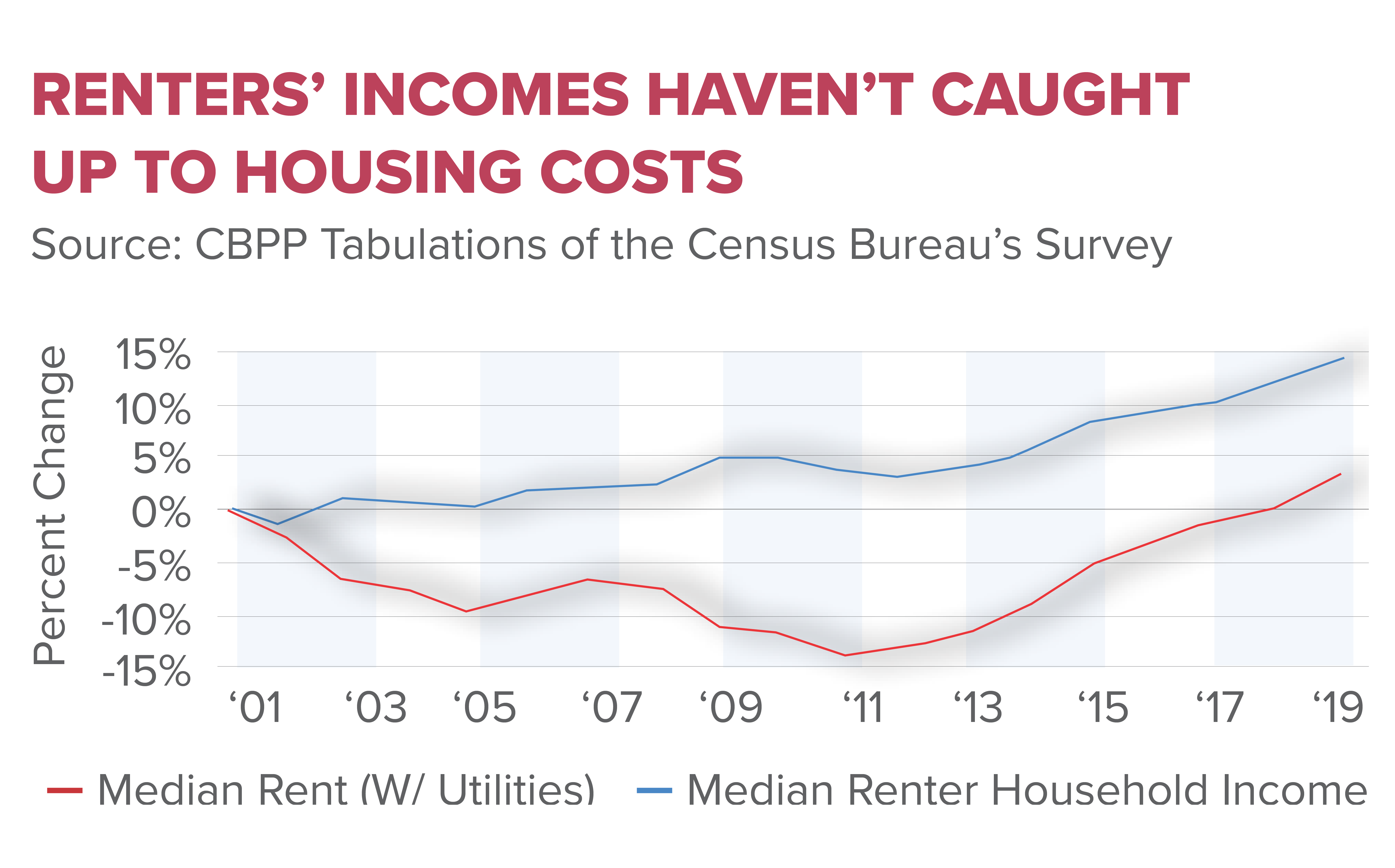
The Housing Affordability Crisis: Causes and Consequences
The housing affordability crisis in the United States has reached alarming levels, with homeownership increasingly becoming an elusive dream for many families. Rising costs, which have more than doubled since 1960, can be attributed to various factors, including heightened labor and material expenses. However, a pivotal aspect of this crisis is the growing influence of NIMBY policies. These policies restrict land development, create convoluted regulations, and ultimately drive up housing prices. As communities resist the construction of new housing projects, the supply struggles to meet the ever-increasing demand, perpetuating the affordability crisis.
Additionally, the implications of the housing crisis extend beyond mere numbers. Many potential homeowners find themselves priced out of markets, leading to increased rental demand and driving up costs further. The effects are particularly felt in urban areas where housing stock is limited. Furthermore, with the decline of construction productivity linked to stringent land-use regulations, the housing market faces substantial challenges in adapting to the needs of a growing population. The situation necessitates urgent reforms to make housing more affordable and accessible.
NIMBY Policies and Their Impact on Housing Development
NIMBY, or “Not In My Backyard,” policies hinder the development of housing projects by creating barriers based on community preferences and often unfounded fears. These land-use regulations stem from community resistance to new buildings, which they fear will alter neighborhood character or increase congestion. While these regulations may seem locally beneficial, they have broad implications for the housing market as a whole, stifling construction productivity and innovation among builders. The effects of such policies are concerning; they not only limit the number of homes that can be built but also gravely impact the affordability of existing housing stock.
The continued prevalence of NIMBY attitudes reveals a paradox in American society: the desire for community and homeownership clashes with the necessity of developing new housing. As regulations tighten, larger-scale construction ventures become less viable, resulting in smaller projects with lower productivity. This trend has led to a decrease in innovation—key to tackling construction inefficiencies—which further complicates the quest for affordable housing. Without addressing the root causes of NIMBYism, the housing crisis will persist, perpetuating the cycle of inadequate housing supply and increased costs.
Construction Productivity Decline and Its Role in the Housing Market
One of the lesser-discussed contributors to the housing affordability crisis is the decline in construction productivity since the 1970s. As large-scale projects became less common, the U.S. construction industry shifted towards smaller, less efficient operations. This downsizing curtailed the economies of scale that once enabled builders to reduce costs and build more affordable homes. Innovative building techniques and mass production methods, which were prevalent in the post-war era, have largely been replaced, leading to stagnation in building output.
This decline in productivity has profound implications for the overall housing market. As fewer homes are constructed and existing properties become increasingly costly, the gap between demand and supply widens. The resultant shortage exacerbates the affordability crisis, pushing many individuals and families toward unaffordable rental markets or housing insecurity. It is vital for policymakers to recognize the correlation between declining construction productivity and the ongoing housing challenges, implementing strategies to bolster productivity through streamlined regulations and innovative practices.
Land-Use Regulations: A Barrier to Affordable Housing
Land-use regulations significantly impact housing availability and affordability. They dictate how land can be utilized, often leading to prohibitive costs for developers and limiting the types of housing that can be constructed. While intended to preserve neighborhood quality and control development density, these regulations can stifle growth and exacerbate housing shortages in high-demand areas. Over the decades, more stringent regulations have emerged, creating a bureaucratic labyrinth that discourages builders from pursuing new projects.
As a result, the ongoing challenges faced by the housing market include reduced number of affordable homes and increased prices for existing residences. The complex landscape of zoning laws, building codes, and community guidelines creates an environment where large-scale developments are nearly impossible. Addressing the negative effects of land-use regulations is crucial for any comprehensive strategy aimed at resolving these housing market challenges and ensuring that more families can achieve homeownership.
Housing Market Challenges: A Complex Web of Issues
The contemporary housing market faces a multitude of challenges, each interwoven with the others, creating a complex web of issues that lawmakers and developers must navigate. The affordability crisis is predominantly driven by escalating property costs alongside a stagnating supply of new homes. Additionally, the influence of NIMBY policies complicates development efforts, leading to reduced construction productivity among builders. Together, these factors contribute to a persistently competitive marketplace where many are unable to secure affordable housing.
Moreover, various regional disparities exist in housing challenges, with urban areas suffering from acute shortages while rural communities may face different issues altogether. As various economic conditions fluctuate, the obstacles within the housing market shift, presenting a moving target for effective policy responses. Recognizing and addressing the multifaceted nature of these housing market challenges is crucial in crafting solutions that can ultimately lead to improved housing affordability and availability.
The Intergenerational Transfer of Housing Wealth
The dynamics of the housing market have led to a significant intergenerational transfer of wealth, creating a wider gap between generations in terms of homeownership. For many younger adults, the financial barriers to homeownership have increased substantially, resulting in a generational divide in wealth accumulation. As older generations benefit from rising property values, younger individuals are often left with limited options, trapped in a cycle of renting and unable to build wealth through home equity. This disparity has long-term implications for economic mobility and social equity.
The situation represents a troubling trend where those who already own homes are able to secure their financial future while younger generations face mounting challenges in entering the market. The question of housing affordability becomes not only an economic issue but also a matter of social justice. Addressing this intergenerational wealth transfer requires comprehensive policies that prioritize the creation of affordable housing and provide support for aspiring homeowners, thus ensuring equitable access to the benefits that homeownership can provide.
Innovation in Housing Construction: The Road Ahead
Innovation plays a critical role in addressing the housing affordability crisis, yet it remains stunted in the construction industry. Despite advancements in technology that have benefitted other sectors, the construction of new homes has lagged behind. The focus on small-scale projects due to regulatory barriers has discouraged investment in innovation and the adoption of cost-saving technologies. If the construction industry adapts by embracing modern building techniques and improving operational efficiency, it could significantly enhance productivity and reduce housing costs over time.
Moving forward, the industry needs to shift its approach to housing development, prioritizing innovative methods such as prefabrication and modular construction. These techniques can not only streamline production but also lower costs, ultimately making homeownership more attainable for a larger population. Collaboration between builders, policymakers, and communities is essential in fostering an environment conducive to innovation, paving the way for a more efficient and affordable housing market.
Transforming Housing Policies for Better Outcomes
To address the pressing housing affordability crisis, thorough reform of housing policies is imperative. Existing policies are often mired in complexities that hinder the ability to respond to market needs effectively. Policymakers must consider the equilibrium between community preferences and the necessity for sustainable growth in housing supply. This includes reducing restrictive zoning laws, promoting higher-density developments, and incentivizing the construction of affordable units.
Effective transformation of housing policies requires a shift in how communities view new development. Engaging residents in dialogue about the benefits of increased housing supply, alongside targeted educational programs that clarify misconceptions regarding new projects, can help foster a more receptive environment. By balancing community interests with the urgency of the housing crisis, we can create policies that genuinely enhance accessibility and affordability for future homeowners.
A Collective Responsibility: Addressing the Housing Crisis
The housing affordability crisis cannot be tackled in isolation; it necessitates a collaborative effort from various stakeholders, including government agencies, private developers, and community organizations. Each party plays a critical role in reshaping the landscape of the housing market, addressing the multifaceted nature of the crisis comprehensively. By working together, these entities can formulate strategies that effectively confront barriers to housing development and promote equitable solutions.
Public awareness and community engagement are vital components of this collective responsibility. Encouraging dialogue about the importance of affordable housing and its implications on community well-being can catalyze change. Additionally, fostering partnerships between public and private sectors, as well as community stakeholders, can create synergies that expedite the construction of new homes. Ultimately, it is through a united approach that society can confront and resolve the pervasive housing challenges that threaten economic stability and quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do NIMBY policies contribute to the housing affordability crisis?
NIMBY policies, which stand for ‘Not In My Backyard’, hinder the development of new housing by imposing strict land-use regulations and heightening community opposition to construction projects. This creates a situation where builders face numerous hurdles in securing permits, ultimately slowing down housing supply and exacerbating the housing affordability crisis.
What impact do land-use regulations have on the housing affordability crisis?
Land-use regulations significantly constrain the ability to develop larger housing projects. This fragmentation leads to smaller, costlier builds and reduces overall construction productivity. Consequently, these regulations contribute to the rising costs of housing, worsening the housing affordability crisis for many Americans.
Can the decline in construction productivity explain the housing affordability crisis?
Yes, the decline in construction productivity is a major factor in the housing affordability crisis. Research indicates that more stringent land-use regulations and NIMBY policies have led to a smaller scale in housing developments. This reduction in scale diminishes efficiency and innovation, causing housing prices to increase and making homeownership less attainable.
What are the housing market challenges exacerbated by construction productivity decline?
Housing market challenges, such as increased prices and decreased availability of affordable homes, are exacerbated by construction productivity decline. As regulations limit the size of projects that builders can undertake, the resulting inefficiencies contribute to soaring costs, thus intensifying the housing affordability crisis.
How does the housing crisis affect different demographic groups?
The housing crisis disproportionately affects younger adults and low-to-middle income earners who struggle with rising costs and stagnant wages. As housing becomes less affordable, these groups face significant challenges in securing homeownership, contributing to wider economic inequality and social divide.
What innovative solutions can address the housing affordability crisis?
Addressing the housing affordability crisis may require reevaluating NIMBY policies, easing land-use regulations, and encouraging larger scale developments. Solutions such as promoting modular and prefabricated construction techniques and increasing investment in affordable housing projects can help boost construction productivity and lower housing costs.
How do external factors influence the housing affordability crisis today?
External factors such as inflation, increased labor and material costs, alongside restrictive land-use regulations and NIMBY policies, combine to drive up housing prices. These elements create a challenging environment for builders and buyers alike, compounding the housing affordability crisis across the nation.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Housing Affordability Crisis | The price of new homes has more than doubled since 1960, leading to a significant affordability crisis for many Americans. |
| Impact of NIMBY Policies | Tight land-use regulations and NIMBYism have hindered the growth of large-scale housing projects, which are crucial for mass production and lowering costs. |
| Decreased Productivity | Since the 1970s, productivity in the construction sector has declined, with home construction becoming less innovative and more expensive. |
| Scale of Construction | The share of housing built in large projects has dropped significantly, affecting economies of scale and leading to smaller, less productive firms. |
| Intergenerational Wealth Transfer | Younger generations have seen a drastic reduction in housing wealth compared to older individuals, highlighting issues of equity in housing. |
| Historical Context | Census data indicates that housing production was significantly higher from 1935 to 1970, coinciding with minimal land-use regulations. |
Summary
The housing affordability crisis has reached alarming levels, making ownership unattainable for a significant number of Americans. Factors such as stringent land-use regulations and the influence of NIMBY policies have restricted the scale and productivity of construction companies, contributing to rising home prices. Historical trends show that decreases in housing production correlate with increases in regulatory measures, further stifling innovation and pushing homeownership out of reach for many. Addressing these underlying issues is crucial for restoring balance in the housing market and ensuring affordable options for future generations.