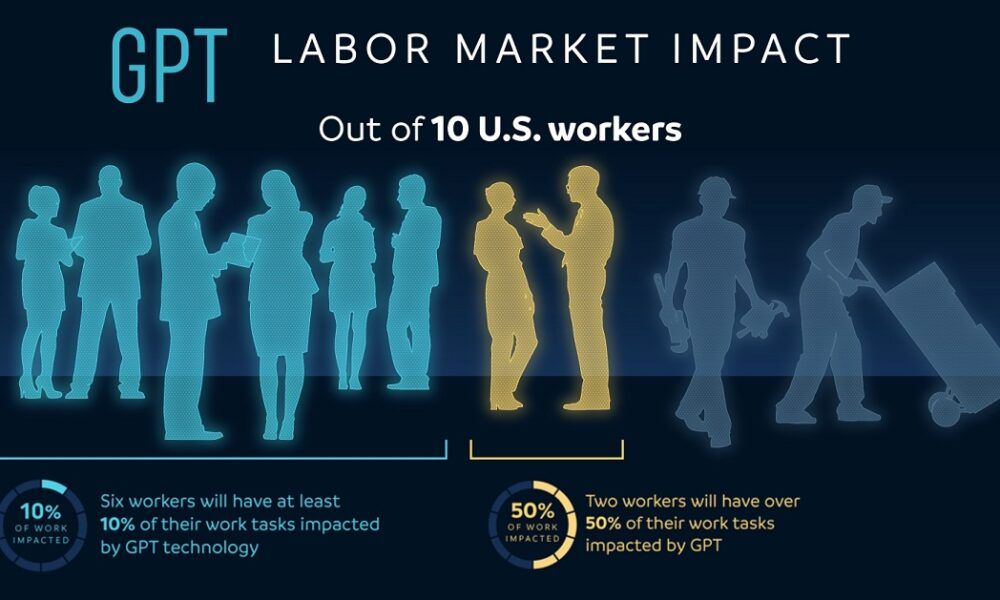
The impact of AI on the labor market is becoming increasingly apparent, reshaping the dynamics of employment in profound ways. As artificial intelligence continues to evolve, its influence on job displacement and creation raises critical questions about the future of work. Researchers have identified key trends in employment that point to significant changes driven by AI and other advanced technologies. Understanding the implications of these developments is essential as we navigate the complexities of occupational churn and the resulting shifts within the workforce. This evolving landscape demands a closer look at how the intersection of technology and labor market trends is affecting job security, skill requirements, and the overall economy.
The advancements in artificial intelligence are ushering in a new era of workforce transformation, prompting discussions around the implications for employment roles and structures. This technological paradigm shift, often referenced as workforce evolution, hints at considerable occupational upheaval due to developing capabilities in automation and machine learning. As AI integrates into various sectors, it’s crucial to explore how these innovations are influencing job availability and the nature of workforce engagement. The notion of ‘occupational disruption’ is becoming central to understanding employment trends, particularly regarding how different job categories are adapting or shifting as a result of this technological infusion. Assessing the ramifications of these changes is vital for workers and employers alike, highlighting the urgency of strategic adaptation in response to labor market trends.
Understanding the Impact of AI on Jobs
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is profoundly reshaping various sectors within the labor market, sparking significant discussions about its impact on jobs. A comprehensive study conducted by Harvard economists has shown that technology, particularly AI, is already causing disruption in the workforce. This transformation is evident as certain job functions evolve or are rendered obsolete. The report highlights that knowledge workers in fields such as finance and journalism must adapt to these changes or risk displacement as AI takes over repetitive and time-consuming tasks.
The changing landscape prompts workers to reconsider their roles within their organizations as productivity expectations rise with the advent of AI. In many cases, AI technologies have demonstrated the ability to enhance productivity significantly; however, they also raise concerns regarding job security and the future of certain professions. This dichotomy of benefits and challenges created by AI means that individuals across the labor spectrum must be aware and prepared for shifts that may redefine their job descriptions.
The Trends in Employment Driven by AI
The recent acceleration of AI adoption has triggered noteworthy trends within the employment landscape. Researchers identified a shift from job polarization—a trend where high-wage and low-wage jobs flourish while mid-income roles languish—to a new growth phase predominantly associated with high-skilled positions. This transition indicates a resurgence in demand for advanced expertise, particularly in fields such as STEM, where job opportunities have surged dramatically. Economists report that the proportion of jobs in STEM fields increased from 6.5% in 2010 to nearly 10% in 2024, reflecting an almost 50% growth, further exemplifying the labor market’s evolution driven by technological advancements.
Conversely, roles in low-wage sectors have seen a decline, especially within retail and service industries. Employment in retail sales, for instance, plummeted by 25% between 2013 and 2023, highlighting the transformative impact of e-commerce and predictive AI technologies. This shift underscores how AI not only creates new opportunities but also fundamentally alters the existing job structure, making it vital for workers to adapt. As the job market continues to evolve with time, staying informed about these trends will be critical for anyone looking to secure their positions in a changing economy.
Navigating Occupational Churn in the AI Era
Occupational churn describes the continuous movement of workers between jobs and industries, reflecting broader economic shifts influenced by technology. Over the past century, this has been a common feature of the U.S. labor market, but recent studies indicate an increase in churn due to the rise of AI. As AI capabilities develop, roles become outdated, while new job categories emerge, leading to a landscape where workers must frequently reskill or upskill to remain relevant. This unpredictable transition period emphasizes the importance of ongoing education and adaptability among the workforce.
Additionally, the nature of work is undergoing a significant transformation. In the face of these changes, workers can no longer rely solely on traditional career paths; they must be proactive in seeking out professional development opportunities. Organizations also have a role in facilitating this process, as investing in employee skill training can mitigate the disruptive effects of AI on job security. Thus, understanding and navigating occupational churn are crucial for staying competitive in an AI-influenced labor market.
AI’s Role in Shaping Workforce Dynamics
The technological advancements in AI are not just reshaping the tools we use but also altering the very structure of workforce dynamics. As AI systems become integrated into various sectors, they inherently change job expectations and working conditions. This phenomenon indicates that organizations must rethink their workforce strategies, leading to a more fluid working environment where the focus is on skills over specific job titles. AI tools facilitate a shift in productivity metrics, urging leaders to adapt their management styles to better accommodate these evolving expectations.
Moreover, the empowerment aspect of AI cannot be overlooked. While it poses risks, especially of job displacement, it also creates opportunities for enhanced creativity and innovation. Companies can harness AI to streamline operations, reduce costs, and increase profit margins. In doing so, outweighing the negative impacts on lower-skilled jobs can be achieved, but only if they’re also prepared to invest in retraining and upskilling initiatives for employees across different levels.
The Future of AI and Employment Trends
As we look ahead, the intersection of AI and employment trends suggests a complex but transformative future. Current research indicates that while certain job sectors may face decline due to the rise of AI, others, particularly those requiring higher skill levels, are expected to flourish. The juxtaposition of declining low-wage jobs alongside the emergence of high-paying, technology-oriented professions outlines a crucial trend in which education and skill development are paramount. Labor markets must adapt to support this transition, ensuring workers are equipped for the evolving job landscape.
In anticipation of future changes, organizations should consider strategic investments in training programs and resources that foster skill development. Educational institutions also play a vital role in adapting curricula to accommodate the changing job market, producing graduates who are ready to leverage AI technologies in their careers. Ultimately, as AI continues to permeate various aspects of employment, embracing change and prioritizing upskilling initiatives will be essential in navigating the ongoing disruption induced by artificial intelligence.
AI Labor Market Impact: A Double-Edged Sword
The impact of AI on the labor market is a double-edged sword, where the advantages must be balanced against the potential risks to employment. On one hand, AI technology can streamline operations, improve efficiency, and foster innovation, leading to job creation in emerging sectors. However, the flip side reflects a concerning trend where jobs in low-wage sectors are diminishing, resulting in widespread economic anxiety. Economists have noted the importance of preparing both current and future workers for an employment landscape increasingly defined by AI and automation.
Additionally, the disparity in job opportunities means that those with skills aligned with technology will have a distinct advantage, creating a potential skills gap. Therefore, it is critical for companies and policymakers to collaborate in developing comprehensive strategies that can address these challenges. Emphasizing equitable access to training programs, resources, and support systems will ensure that workers are not left behind as AI continues to redefine the world of work.
Automation Anxiety: Addressing Workforce Concerns
The phenomenon of automation anxiety has emerged as a psychological response among workers as AI technologies proliferate and reshape industries. Many fear that machines will replace human skills, particularly in jobs requiring repetitive tasks. As highlighted in recent studies, this anxiety reflects a significant concern about job security and the uncertain future of employment. Addressing these fears involves transparent communication from employers about the implications of AI, alongside committed efforts towards workforce development and training.
Moreover, organizations should create a culture of adaptability by encouraging continuous learning among employees. By fostering an environment where workers feel empowered to enhance their skill sets, companies can alleviate some of the anxiety surrounding job displacement. Emphasizing the collaborative potential of AI and human workers can showcase the technology as a complementary force rather than a threat, ultimately leading to a more secure and optimistic outlook for the workforce.
Investing in Skills for an AI-Driven Future
As AI technology continues to shape the labor market, investing in skills development becomes essential for both individuals and organizations. The increasing reliance on AI means that traditional job roles are evolving, necessitating a focus on competencies that align with the demands of new technologies. Companies with foresight will prioritize training initiatives that prepare their workforce for changes, ensuring they remain competitive in an AI-driven economy.
Additionally, adapting educational programs to address the skills gap induced by AI will be crucial. This includes fostering partnerships between educational institutions and industries to make sure that the curricula reflect current and future job requirements. By focusing on relevant skill sets, companies can build a workforce that not only meets the needs of today but is also prepared for the challenges of tomorrow, creating a resilient labor market in the face of ongoing technological disruption.
Evolving Job Roles in the Age of AI
In the age of AI, job roles are undergoing substantial transformation as organizations adapt to new technologies. The increase in automation and AI capabilities means that many traditional positions are being redefined or rendered obsolete, leading to a reassessment of existing job structures. Many roles will not disappear entirely but will evolve, requiring workers to develop new competencies to stay ahead in their careers. This evolution necessitates a proactive approach from both individuals and organizations to foster a culture of continuous learning.
Employers must take the lead in facilitating these transitions by providing upskilling resources and support to help employees navigate their changing roles. Simultaneously, it is essential for workers to be open-minded and ready to embrace new approaches to work and learn from one another. As job descriptions morph, successful adaptation to these changes will be crucial in making the most of the new opportunities presented by AI technologies while mitigating the impact of job displacement.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the impact of AI on jobs in the labor market?
The impact of AI on jobs in the labor market is profound and multifaceted. Recent studies indicate that AI is not only transforming the workforce but also changing the distribution of jobs significantly. For instance, while there was a phase of stability from 1990 to 2017, recent trends show an increase in STEM jobs and a decrease in low-paid service roles, suggesting a shift in the types of skills that are in demand.
How is technology and labor market dynamics evolving due to AI?
Technology and labor market dynamics are evolving rapidly due to AI advancements. The study co-authored by economists at Harvard suggests that AI is driving occupational churn, leading to both an increase in high-paying jobs that require advanced skills and a decline in traditional low-wage positions. This reflects an ongoing transformation where jobs are increasingly concentrated in skilled sectors.
What trends in employment have emerged from AI’s impact on the labor market?
Several trends in employment have emerged as a result of AI’s impact on the labor market. These include increased job opportunities in STEM fields, a downturn in low-paid positions, and a significant decline in retail jobs. The evidence suggests that companies are investing more in AI technologies, resulting in a shift towards high-skilled labor, while many traditional roles, especially in service and retail, are declining.
What is occupational churn and how does it relate to AI workforce changes?
Occupational churn refers to the rate at which workers change jobs and the dynamics of job distribution in the labor market. It relates to AI workforce changes as recent research shows a shift in occupational churn patterns due to technological disruptions, driven by AI. As companies increasingly adopt AI technologies, there is a notable increase in high-skill job opportunities while many lower-wage jobs are at risk of decline.
Are there long-term effects of AI on employment in the labor market?
Yes, there are significant long-term effects of AI on employment in the labor market. Over time, AI is expected to enhance productivity, but it also poses risks of job displacement, particularly for workers who may struggle to adapt to new technologies. As companies demand higher productivity, knowledge workers will face increasing pressure to leverage AI, altering traditional job expectations and responsibilities.
How does AI influence trends in employment patterns across industries?
AI influences trends in employment patterns across industries by accelerating the growth of jobs in high-demand sectors such as technology and reducing the availability of jobs in more traditional fields like retail. This dual effect results in a structural transformation of the labor market, where skills aligned with AI technologies become more critical for job seekers.
What are some examples of sectors negatively affected by AI in the labor market?
Sectors negatively affected by AI in the labor market include low-paid service roles and retail jobs. For instance, retail sales positions have seen a significant decline, with the share of these jobs falling markedly due to the rise of e-commerce powered by AI. Similarly, many low-paid positions in service industries are shrinking as companies adopt automated solutions to reduce labor costs.
What does the future of the labor market look like with the rise of AI?
The future of the labor market with the rise of AI appears to emphasize the need for higher skills and adaptability among workers. As AI continues to influence job patterns, we can expect a growing demand for STEM professionals and skilled workers, while many traditional jobs may diminish. Continuous learning and skill development will be imperative for navigating this evolving landscape.
| Key Trends | Description |
|---|---|
| Job Polarization Ends | Shift away from low-paid jobs towards well-compensated roles requiring advanced training. |
| Rise of STEM Jobs | Increase in STEM job share from 6.5% in 2010 to nearly 10% in 2024. |
| Decline in Low-Paid Service Roles | Stagnation or decline in employment for low-paid jobs post-2019. |
| Retail Job Decrease | Retail sales jobs fell from 7.5% to 5.7% of the market between 2013 and 2023, influenced by e-commerce and AI. |
Summary
The AI labor market impact is becoming increasingly evident as technology reshapes the workforce landscape. A recent study by Harvard economists highlights that AI is not just a futuristic concept, but is already actively transforming job distribution and market dynamics. With trends such as the end of job polarization, an increase in STEM-related positions, a decline in low-paid service roles, and significant shrinkage in retail jobs, the evolution driven by AI profoundly affects every aspect of employment. Therefore, understanding these shifts is crucial for workers across all sectors to adapt to the changing demands of the labor market.